Haley Belisle, a recent graduate of Ohio Northern University, was baffled this spring when the Hardin County Board of Elections rejected her application to vote absentee in the state’s presidential primary.
The problem was her signature on the application: It didn’t match her voter registration signature.
“When I originally registered, I was just out of high school, and I apparently signed my name in a very curly cursive, which I don’t do any more,” she said.
The 24-year-old got a new application and replicated the original style, she said, effectively “forging my own signature.”
Belisle was able to cast her ballot.
That wasn’t the case for all potential voters in Ohio’s presidential primary.
This summer, Eye on Ohio set out to examine how many absentee ballot applications were rejected, why, and how voters could avoid those mistakes. The of millions of Ohio applications from the state’s 88 counties revealed a patchwork and unreliable system for tracking the requests that makes it nearly impossible to accurately know how many voters, if any, were disenfranchised. It also called into question the accuracy of information collected by state election officials on rejected applications.
With only weeks until the 2020 presidential election, and lingering concerns about the novel coronavirus, voters are applying for absentee ballots at a record pace.
That, along with President Donald Trump’s attacks on the use of mail-in ballots, though not supported by research, could bring magnified attention to the process, especially in a swing state like Ohio where Trump and Sen. Joe Biden are swapping narrow leads in the polls.
Applications for mail-in ballots received relatively little attention in the past, as most fair election advocates concentrated efforts on whether absentee and provisional ballots were counted. Ohio is one of 34 states that allows any eligible voter to use mail-in voting. And the state is one of nine that mails applications for ballots to registered voters
The pandemic caused the number of domestic applications for absentee ballots to surge, amplifying the importance of this first step in the mail-in voting process. In the spring, the number of absentee votes cast was five times higher than the last presidential primary in 2016.
State and county officials have been aware of data collection issues for years but haven’t acted to fix them.
Simple questions, like the total number of absentee ballot applications for the 2020 primary, were hard to reconcile when Eye on Ohio examined:
- Public reports released by state election officials;
- Surveys submitted to the state by county boards of election;
- 1.79 million individual records spread across 1,370 spreadsheets containing individual voter absentee ballot applications that state lawmakers in March required counties to submit to state officials daily.
In a baffling move, state election officials excluded the number of rejected absentee ballot applications when reporting the number of people who applied for a ballot.
County election officials reported to the state that they rejected as invalid 72,077 applications for absentee ballots for the 2020 primary, according to state election records obtained by Eye on Ohio.
That accounts for just over 4% of all absentee ballots requested. (For comparison, about 1.2 % of absentee ballots – – cast by voters in the spring were tossed out.)
A deeper look at the application rejection numbers showed that they, too, are problematic.
Local election officials told Eye on Ohio they used different methods for reporting rejected or invalid applications.

Some counties, like Cuyahoga, provided the state with a total number of rejected applications. Others, like Hamilton, counted as invalid only applications where errors were not resolved or “cured” before the application deadline.
Many counties said they decided not to count applications that, for whatever reason, arrived late, an issue likely exacerbated by slowed U.S. Postal Service service delivery.
Ohio’s counties also did not have a standard way to track or report the reasons applications were rejected – and some counties didn’t track the reasons at all – though all said they kept the rejected applications on file.
A spokeswoman for Ohio Secretary of State Frank LaRose declined to answer specific questions about inconsistent absentee ballot application numbers.
What does that all mean for Ohio’s voters?
- We don’t know how many voters in the first Ohio election with a majority mail-in vote tried – but failed – to get an absentee ballot to cast.
- It is impossible to gauge whether counties applied the same standards to correcting application errors or rejecting ballot applications.
- The same could be true for the 2020 presidential election, which is expected to be decided by an unprecedented number of absentee votes.
Counting Down

Applications for mail-in ballots for the presidential election have soared in Ohio.
As of Sept. 22, Ohioans had submitted 1.8 million absentee ballot applications, far surpassing requests received months before previous presidential elections, according to LaRose’s office.
That trend began during the spring primary, when mail-in ballots accounted for 85% of the total votes cast, a 444% increase from the number of domestic absentee ballots cast in 2016, .
In the past, when the lion’s share of ballots was cast in-person, the gap between ballot applications and ballots sent to voters was negligible.
Ballot application information is highly sought after by political parties and campaigns to send campaign mailers and party slate cards to voters who request ballots, a technique called “absentee chase.” It is also used now to help individual voters track applications (and later ballots) through the system.
Normally, during an election, the Secretary of State’s office gets information weekly on the number of absentee ballot applications submitted to local boards. During the extended presidential primary this year, Ohio lawmakers required the county boards to submit the information daily, though not all did.
Fully assessing ballot application records from all 88 county elections boards is so arduous that LaRose’s office doesn’t attempt it. It also doesn’t review the records for accuracy, spokeswoman Maggie Sheehan said in an email.
Instead, state election officials use a series of surveys filled out by county elections board officials to release its official post-election report that tallies the total number of votes cast and those counted, including an accounting of absentee or mail-in ballots and provisional ballots used when there’s a question about a voter’s eligibility.

The office makes a habit of publicly sharing the number of ballot applications received before elections — but not sharing the number of invalid or rejected applications after the election.
LaRose’s office told Eye on Ohio that was to maintain consistency with past post-election releases.
His office declined to answer a litany of technical questions about the accuracy of the ballot application data it collected from the counties during the primary, insisting the counties were the “owners” of the data. That included instances where the state and individual counties provided Eye on Ohio with significantly different numbers of rejected ballot applications.
In multiple interviews with reporters, which a spokeswoman insisted be on background, state elections employees acknowledged that relying on inconsistent and incomparable application records was problematic.
LaRose’s office has blamed what of records collection as one of the problems contributing to a voter record system that the secretary of state has, in the past, characterized as “unacceptably messy.”
Ohio’s balkanized elections data has caused headaches before, including in 2019, as the state carried out an effort to purge inactive voters from its roles. Not only were “data mistakes” discovered that would have led to active voters being purged, but each county used a different process or set of standards for removing voters from its local list of eligible voters.
“Secretary LaRose has been on record stating he would like to reform Ohio’s voter registration system to be top-down,” Maggie Sheenan, his press secretary said in an email.
The current system has persisted, in part, because there’s disagreement on whether to change it, said Aaron Ockerman, executive director of the bipartisan Ohio Association of Election Officials. Not for any nefarious reason, he said.
About 15 years ago, Ohio implemented a statewide voter registration database, a requirement of federal legislation called the Help America Vote Act, which also created the U.S. Elections Assistance Commission.
The federal government did not mandate a unified or “top down” system, and so the job of collecting Ohio’s election data has largely been left in the hands of county election officials.
After 15 years of discussion and debate, officials have been unable to reach a consensus about whether or not to change the system, Ockerman said.
“And I am not sure we are any closer now,” he said.
In general, most of the smaller counties do not want to give up managing their own data, Ockerman said, while larger counties are more open to using one system because they spend a lot of energy and money on data collection.
From the standpoint of individual voters, Ockerman said, boards are very responsive to helping track applications and ballots, and have advocated for the ability to reach voters to make corrections through phone calls and emails, when in the past they were limited to sending letters.
Ockerman acknowledges that there also has been “growing pains” when it comes to understanding at the county and state levels the nuances of the absentee ballot and application data and that problems or confusion can result from the disparate methods used to collect the information.
“This is not something that can’t stay under the rug for a lot longer,” Ockerman said. “There will be increasingly more attention.”
The lack of data also prevents assessments of how well the system is working statewide, which could lead to improvements in the voter experience, including quickly connecting the dots on issues that lead to application rejections. For instance, Ockerman said, many county elections boards have noticed that voters for the upcoming election have struggled with the design of applications provided by special interest groups, resulting in a higher number of invalid applications and more work for local elections officials to help voters correct them.

The secretary of state’s office has not issued a directive to standardize the way counties collect the information about mail-in ballot requests. LaRose has issued other directives, including one in July to streamline the way counties can respond to invalid requests – using phone calls and email – for the presidential election and speed up the turnaround time for correcting application errors.
And, earlier this month, LaRose issued another order limiting county boards to provide only one dropbox per county for collecting absentee ballots. Though he personally supports offering more than one dropbox per county, LaRose said it would require a legal ruling or law change to do so. But a. “It is his job to work with each board to address any local issue that significantly impacts voters in that county being able to cast their ballots,” U.S. District Judge Dan Polster wrote.
What’s stopping LaRose from directing boards to use a consistent method for reporting invalid applications?
Sheehan didn’t respond to that question.
Different Rules
Each elections board is free to track its ballot applications in the manner it chooses – whether in a paper file, a handwritten list, an electronic spreadsheet or specialized software. The secretary of state’s .
There’s also no set way to track invalid or rejected applications, including the reason the application is rejected and whether a voter could be reached to fix the problem.
The Morrow County Board of Elections, for example, told Eye on Ohio that it kept no records of reasons absentee ballot applications were rejected.
“We rarely have applications rejected,” Karen Cavendish, a board employee told Eye on Ohio in an email. “If something is missing on the application, we track the voter down and get the application corrected so it can be processed.” The county, which has more than 24,000 registered voters, reported that it didn’t receive a single invalid absentee ballot application for the spring primary.
Wood County, like many other smaller boards, said it keeps incomplete applications but could not share the reasons that 115 primary applications were rejected or how many were corrected.
Boards of elections reject ballot applications for many reasons, including those missing a signature or proper identification, like a driver’s license number or last four digits of a social security number. The boards also cannot send ballots if the voter doesn’t indicate which ballot they want: Republican, Democrat, Libertarian or one with only nonpartisan issues and local questions.
Tracking the path of ballot applications is further complicated because some elections boards correct flaws, such as a missing party affiliation, over the phone. Other issues, such as a missing signature, have to be corrected in person or with a fresh application.
Mismatching numbers
In many cases, information individual counties provided to Eye on Ohio did not match what they reported for numbers of “invalid” ballot applications to state election officials for the spring primary.
Some counties, like Cuyahoga, tracked specific reasons that ballot applications were rejected, like having an invalid date of birth or not specifying a political party.
The Cuyahoga County Board of Elections reported to state election officials that it rejected 18,980 applications to vote in the spring primary, close to 9% of all applications. However, 11,847 of those voters corrected their applications or submitted new ones, according to data provided by the board, which left more than 7,133 applications that didn’t result in ballots being sent to potential voters or just over 3% of all applications.
Hamilton County, on the other hand, reported 4,432 invalid ballot applications or just under 3% of all applications the county received. That number does not include applications that initially had errors that were later corrected, said Sherry Poland, the director of elections. It also does not include more than 1,800 applications that arrived at the board after the application deadline passed that the county provided in response to an Eye on Ohio records request.
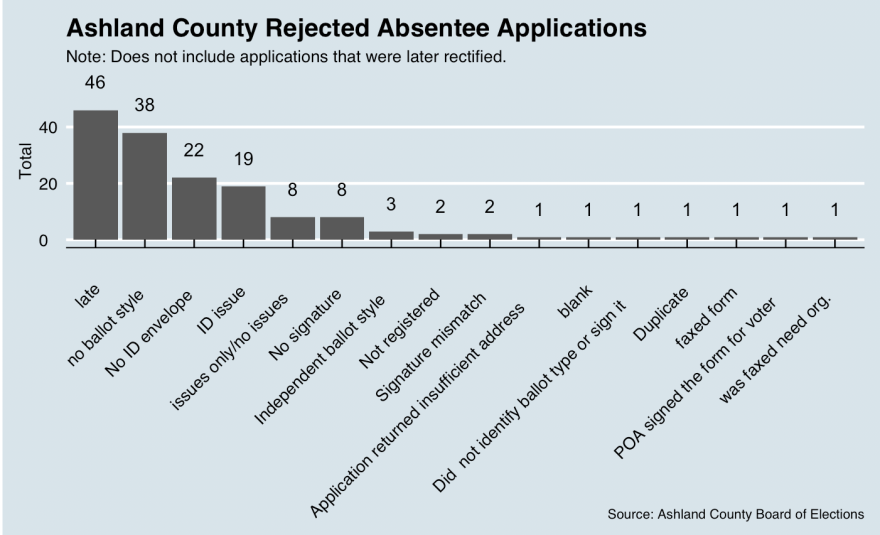
Ashland County, with a little over 34,000 registered voters, tracked absentee ballot applications on a spreadsheet, noting the problem with the application, how the voter was contacted, the date a new application was mailed and whether a new application was returned. A spreadsheet provided to Eye on Ohio lists close to 160 invalid applications, with about 50 listed as “fixed” before the election. But the county reported a total of 58 invalid applications to state election officials.
The spreadsheet is akin to “notes” and may not include problems with applications that were corrected after the application deadline, Ashley Jones, deputy director of the board, said in an email.
Jones said the official number the board reported to the state comes from a bi-partisan count of the paper file of rejected applications.
Two other issues complicate efforts to accurately account for how the absentee ballot application process impacts Ohio voters.
Voters also may request ballots multiple times, either to correct an earlier error or because of confusion over multiple election mailings, an issue in the 2020 general election. Eye on Ohio found that in the spring at least 13,067 Ohio voters applied twice for a ballot for the presidential primary, and 34 people applied for a ballot three times.
It’s also unclear from the available data how many voters applied for mail-in ballots, were unable to get one, and voted in person. That number likely is small, at least for the 2020 primary, because in-person voting was extremely limited.
Questions of fairness
In a closely watched presidential election, the lack of consistency could lead to a contested outcome, similar to the 2000 presidential election, in which “hanging chads” put the outcome of the election in the hands of the U.S. Supreme Court.
Legal challenges related have already been mounted, including a filed in July by the League of Women Voters of Ohio and the A. Philip Randolph Institute over what the groups called a “flawed system” of matching voter signatures on ballot applications and ballots that led to both being rejected during the primary.
Attorneys for the American Civil Liberties Union of Ohio, which is handling the lawsuit, have asked a federal judge to declare the current signature matching process unconstitutional and to order the state to stop using the process until a fair and uniform process can be put in place.
In late August, the ACLU filed a request for a preliminary that would require voters to be notified by mail or phone of problems with signatures on their applications or ballots. And for voters to be given more time to “cure” any potential issues with signature matches on applications and ballots.
The lawsuit cites an by Alexander Street, a Montana-based political science professor who conducts statistical research on voter data. Street was hired to analyze county-level information on both mail-in ballots and applications.
Street’s analysis, though limited to signature matching issues, found that absentee ballot applications were likely rejected at an even higher rate than absentee ballots cast by voters, creating an extra layer that “will impose the burden of resolving the problem on the would-be voter.”

Street’s analysis of county-level records, he said, revealed that “much like an iceberg, this previously hidden layer is much bigger than the layer which was already visible.”
Like Eye on Ohio’s analysis, Street’s results were limited by data counties provided, which he deemed “often opaque, inconsistent and incomplete.”
Street estimated boards rejected at least 10,038 absentee ballot applications based on “signature issues” alone in federal elections dating back to 2016.
A to the injunction request, filed on behalf of LaRose, called the signature matching issue “trivial.”
“It cannot be emphasized enough that the failure to submit a valid absentee-ballot application does not disenfranchise any voter—the voter will simply have to vote in person. Considering all voting opportunities available, matching signatures on absentee-ballot applications results in no burden at all on voting,” the Ohio Attorney General’s office, which represents LaRose, said in a response filed on Sept. 12.
The response estimated a total of 217 ballots rejected for signature mismatches in the 2020 primary election. The response did not estimate how many applications were rejected because of problems with signatures.
that the signature matching poses a “moderate” burden but not enough to strike down practice as illegal, which could be viewed as “particularly damaging” so close to the Nov. 3 election.
Eye on Ohio was unable to fully account for the number of absentee ballot applications that counties rejected because of signature mismatches. That’s in part because not all counties tracked reasons for rejections. In some cases, counties used a single column in a spreadsheet to make notes about errors with both applications and ballots.

Athens, Carroll, Clark, Clinton, Fayette, Hardin, Jackson, Lucas, Montgomery, Perry, Pickaway, Seneca, Shelby, and Warren counties together had 455 labeled “sig issue”; Cuyahoga had 598 tagged as “sig invalid”; Ashland labeled two “signature no compares”; Huron had nine “signature miscompares.” The number is likely higher since only 19 counties provided applications that specifically cited an incorrect signature problem. Also some counties labeled their applications as simply, “problem,” “incorrect,” “application rejected,” or something similar.
Signatures that appear not to match are just one of more than 17 reasons listed in county-level records for rejecting applications
Eye on Ohio’s review of the available application rejection data supplied by counties showed that in the 2020 primary election the most common reason, by far, that applications were rejected was that voters didn’t check a box stating which political party (or nonpartisan) ballot they wanted. The next most common mistake was an incorrect birth date.
One reason that examining ballot application rejections could matter, is to see whether voters are being treated differently across the state.
The signature mismatch lawsuit argues that voters should not be “subject to the whims of different county election officials when it comes to their fundamental right to vote.”
Different treatment that could affect whether voters get to cast a ballot or whether a ballot is counted is a violation of a clause of the U.S. Constitution, which provides equal protection and that people in similar situations be treated equally under the law, according to the lawsuit.
“It’s the law that when it comes to voting you have to have the same opportunity as other voters, Freda Levenson, legal director for the ACLU of Ohio, said, “You can’t be favored or disfavored.”
The record-keeping at the county level is “simply inadequate” making it impossible to know the true extent of any issue,” said Levenson, whose own application for a primary ballot in Cuyahoga County was initially rejected because officials didn’t think the signature on her application matched the one on her voter registration. She was able to fix the problem in time and cast a vote.
“But that is not the case for all citizens,” she said.
Data headaches aren’t new
This isn’t the first time Ohio’s maddening lack of standardization has stymied watchdogs or election-watchers from understanding the effect of Ohio’s ballot application process.
The Associated Press The news service reported that many counties could not say how many applications were rejected, and others didn’t track the reasons for rejections they did log.
Still, the investigation found that more than 7,000 applications for ballots were rejected in an election where far fewer voters relied on mail-in ballots.
The Stanford-MIT Healthy Elections Project said it could not analyze the reasons that Ohio absentee ballot applications were rejected because not enough information was available.
The project, led by professors from Stanford and MIT, was launched to ensure the 2020 election could “proceed with integrity, safety, and equal access,” according to its website.
Collecting accurate, consistent and comparable data would benefit efforts to improve the election process and to enfranchise voters, said Steven Huefner, an Ohio State University law professor and election law expert.
Researchers who study political science and elections administration, legal issues related to voting, and legislative decision-making all are desperate for better data to rely on to better understand how the current mail-in voting system works and what reforms might help.
“That can’t happen until we know where the real gaps are or where people are typically falling down,” Huefner said.





